The following content is sponsored by Range ETFs
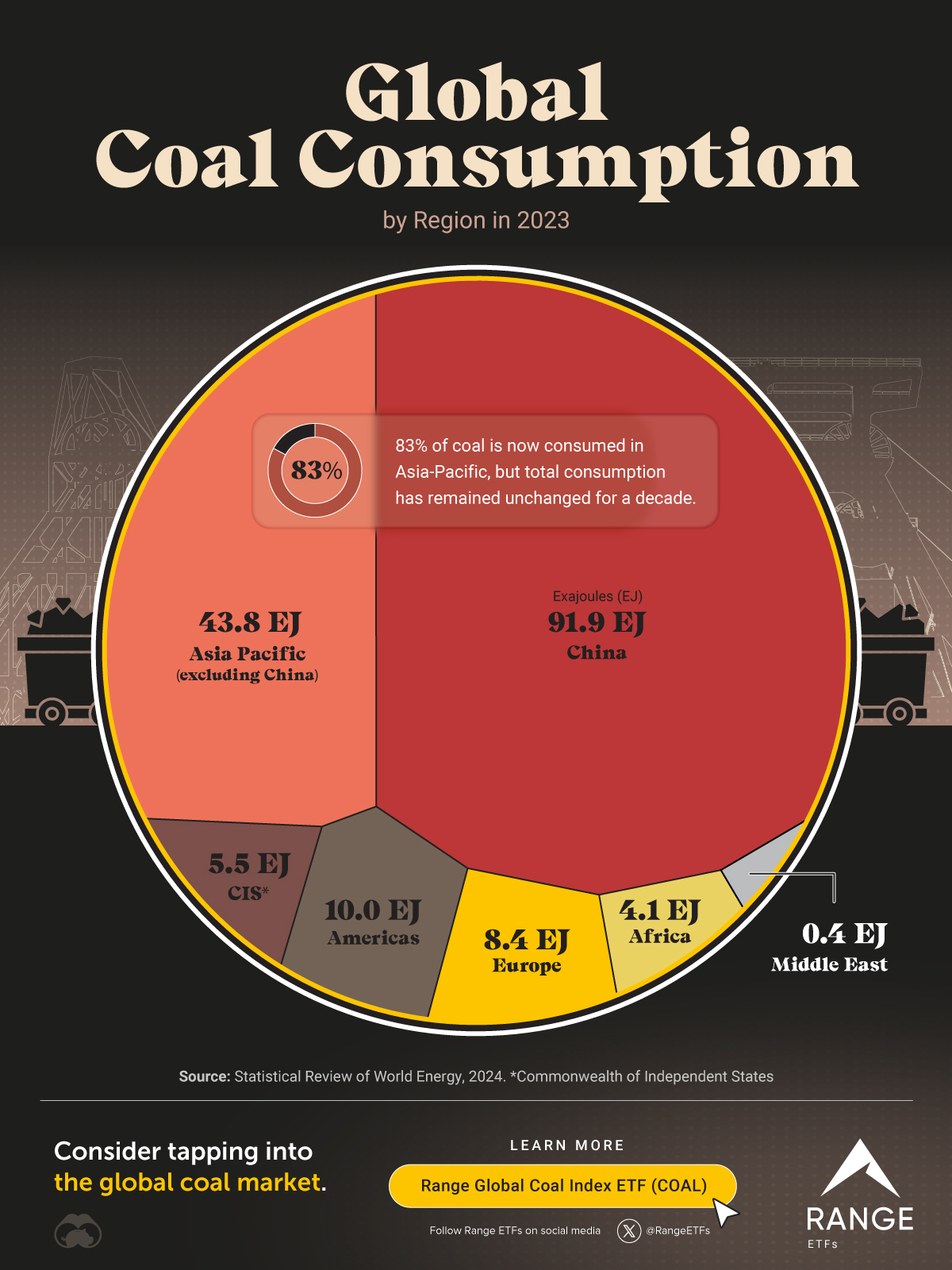
World Coal Consumption by Region in 2023
Despite many nations transitioning away from fossil fuels, in 2023, world coal consumption reached a staggering 164 exajoules (EJ) of energy, a record high for any year.
For this graphic, Visual Capitalist has partnered with Range ETFs to explore the role coal plays in the global energy mix and determine which regions still consume large quantities of coal.
The Role of Coal in Global Energy
Coal is a significant player in the global energy mix, contributing 26% of the world’s energy in 2023, more than all non-fossil fuel sources combined. The only energy source that contributed more to the global energy mix was oil.
Here’s how that consumption breaks down by region:
| Region | Consumption (1018 joules) | Share % |
|---|---|---|
| China | 91.9 | 56.1% |
| Asia Pacific (excluding China) | 43.8 | 26.7% |
| Americas | 10.0 | 6.1% |
| Europe | 8.4 | 5.1% |
| CIS* | 5.5 | 3.4% |
| Africa | 4.1 | 2.5% |
| Middle East | 0.4 | 0.2% |
| Total | 164.0 | 100% |
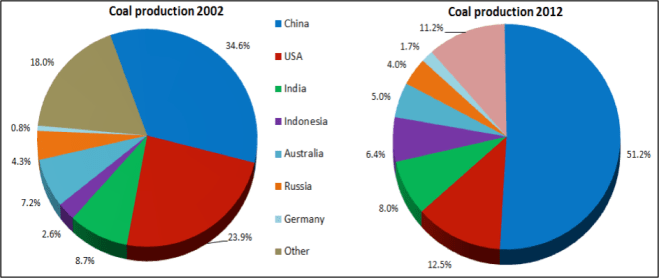
Coal consumption has decreased in many regions. For example, both North America and Europe reduced their energy consumption from coal by 16% in 2023. However, a heavy reliance on coal in the Asia Pacific region has led to global coal consumption remaining essentially the same over the past 10 years.
When I saw this statistics I immediately looked up: What is the U.S role in global coal consumption and found out it was 8.2 EJ om 2023 or 5.0% of world consumption.
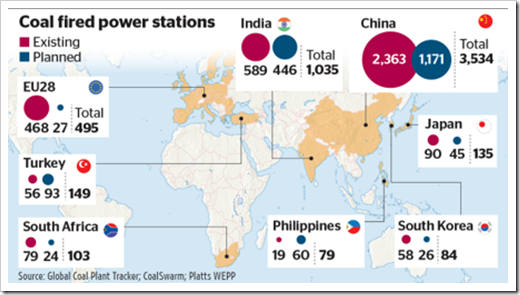
China’s coal consumption is more than eleven times larger than the U.S Coal consumption. In fact, their appetite for mining coal is that they even mine coal with a noticeable Uranium content, and burn it without separating out the Uranium first, leading to severe health problems for the people downwind from the coal burning power plants. In addition, since scrubbing is expensive the operators have the scrubbers down for maintenance as often as they can get away with it.
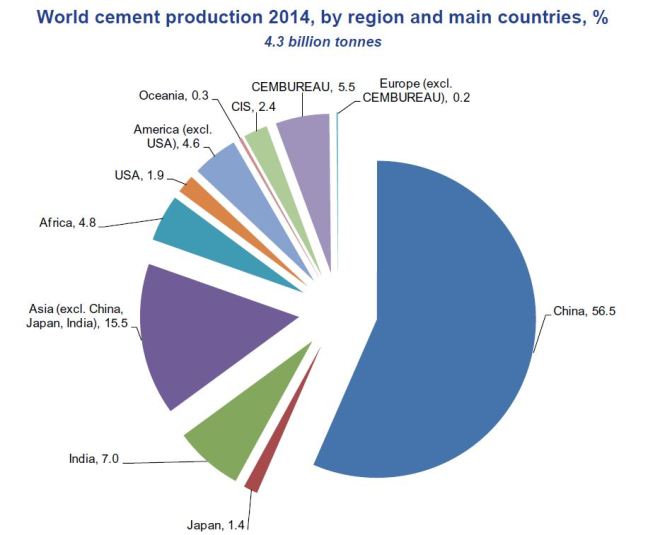
China is also the world leader in cement production. In 2022 China produced 2,1 billion metric tons of cement, or 64% of the world total. By comparison, U.S. produced 95 million metric tons, or about 22 times less than China.
But where China has U.S and the rest of the world over a barrel is in the mining and production of rare earth metals. China mined 240,000 metric tons in 2023, or about 64% 0f the worlds total, but China is also the world’s largest importer of rare earth metal ore for refining. By comparison, US mined 43,000 metric tons, but most of it is still refined in China. The US regulatory environment makes it a slow process to get permits. China has strict export controls over who can be allowed to buy refined rare earth metals, and they always want a favor in return for doing so.
We have our work cut out for us. Right now we are too dependent on China to fully be able to sever our dependence on China.